Which disease's red
spots on the body are a sign?
Red spots on the skin may be caused by
infections, health conditions, irritation, or allergies. Red spots on the skin
can range in size from small to large and may cover a small to a significant
area of the body. Insect bites and stings may cause varying sizes and types of
red spots on the skin. Heat rash vs. sun rash Sunspots on the skin that itch or
burn after being outdoors may be caused by sun exposure or heat.
A common type of rash causes redness and
itchiness in response to an environmental irritant touching the skin, such as
poison ivy, soap, makeup, or household chemicals. Erythema multiform rashes do
not leave a scar, but can, in some children, leave dark spots on the skin for
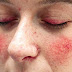
several months. Rosacea causes pimples and redness on the face and is prevalent
in lighter-skinned people. Rosacea is a skin disease that causes skin
irritation, redness, and small pimples.
Keratosis pilaris
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is a common skin
condition that causes small red, white, or flesh-colored bumps on your skin.
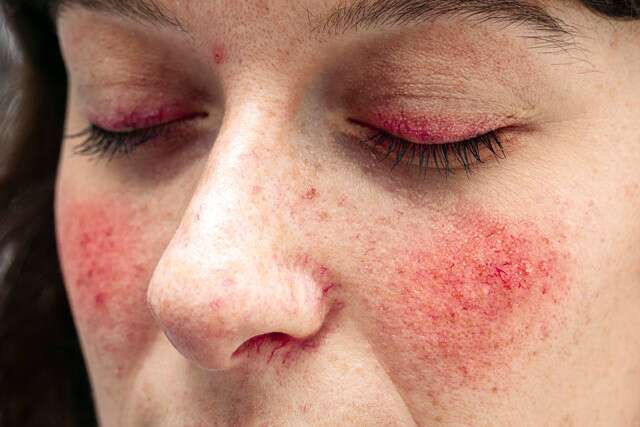
Seborrheic dermatitis is a rash that appears as splotches of redness and
scaling around the eyebrows, eyelids, mouth, nose, trunk, and behind the ears.
A distinctive rash develops, most often on your face and eyelids, as well as
your knuckles, elbows, knees, chest, and back. The rash can be grey, dark
brown, or black in people with darker skin.
When the rash goes away, the skin around
certain spots may appear darker for several months, but no scars are left. The
sudden appearance of these bumps may appear like a rash, warts, or a contagious
skin disease called molluscum contagious. Redness can occur on your hands,
feet, and arms, or folds in your skin, like on the back of your knees.
Depending on the primary cause, red spots may develop suddenly or develop over
an extended time.
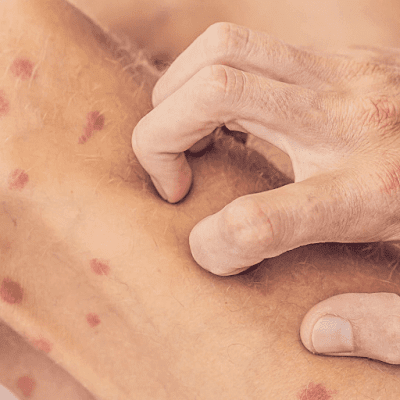
If you have small red, purple, or brown patches
on your skin, tiny red patches could be petty skin rashes. Tiny, pinpoint red
dots are caused by blood vessels breaking off right below your skin. Petechiae
are caused by broken capillaries, the tiny blood vessels beneath your skin.
Tiny, punctured blood vessels are visible on the skin, called petechiae.
Hemangioma
Red patches in the skin occurring in isolation
may be small, and benign Tumours of blood vessels known as Red spots similar to
the ones in rashes can also have other characteristics, like unusual texture or
raised skin, which can be found in people of all skin colors.
Whether the mysterious, unidentified red spots
are on your arms, legs, or face, these red lumps can be part anxiety and part
frustration. They often appear as red, scaly, itchy patches on your joints and
around your scalp.
What to do if there is
a red rash?
Certain medications, including antibiotics such
as amoxicillin, may also trigger an itchy rash on your skin. Your skin might
feel dry, irritated, and red, and you might have a skin rash. If you notice a
skin rash that is itchy or hurts, think twice about going to the pharmacy and
getting a few creams unless you know what is causing it.
Seborrheic dermatitis may also result in dry,
flakes of skin in the areas around the faces, breasts, and inner folds of your
arms, legs, or groin. Eczema can cause dry, chafed, lumpy areas around the
elbows and knees, or more severe cases of red, scaly, and puffy skin throughout
your body. For example, candidiasis, a common fungal infection, causes an itchy
rash, which usually appears in the skin folds.
1. Knowing what type of rash you have may help
the dermatologist select the best treatment for healing the rash. Often, you
can tell what is causing a rash by the way it looks and the symptoms it causes.
2-A cold bath or shower can help to temporarily
alleviate any itchiness, but over-showering or bathing should be avoided
because this reduces natural oils that protect your skin and may worsen the
condition. Taking lukewarm baths can help relieve itching, but avoid using
soaps as they may aggravate your skin's irritation.
3-You may be able to wash off much of the
rash-causing substance if you wash the skin immediately after coming into
contact with it. If you get red, itchy welts on your skin, particularly where
some possible irritants or allergens come into contact, you might have contact
dermatitis.
Depending on what caused your rash, treatments
might include a med-free cream or lotion, medication taken orally, or surgery
on your skin. Treatments may include moisturizing creams, lotions, baths,
cortisone creams, which reduce swelling, and antihistamines, which reduce
itching.
What to eat and what not to eat if there is a red rash
Elimination diets and foods that are used to
prevent a food-sensitive eczema response usually take place approximately six
to 24 hours after the individual has eaten the specific food. To identify which
foods might cause a reaction, your health care provider will usually recommend
an elimination diet. This diet involves the avoidance of some of the more
common foods known to trigger eczema.
The easiest way to cure food allergies or
intolerances is to remove the offending food/s from your diet. The best way to
treat an egg allergy is to avoid eating eggs or any food that contains eggs.
If you or your child
has signs or symptoms of a food allergy soon after eating eggs or products that
contain eggs, consult a healthcare provider. If your child has these reactions
after eating food, they should get tested for a food allergy.
Oranges and other foods high in vitamin C
can help protect skin from irritation. According to a March 2015 review in A
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, probiotics can change your skin
microbiome for the better. According to the review, probiotics can help prevent
or treat itchy skin, breakouts, and other symptoms of conditions such as
eczema, acne, or sun damage. Taking a probiotic supplement and avoiding
processed foods and dairy can help rebalance gut-friendly bacteria and
alleviate symptoms of inflammatory skin conditions.
This is particularly true if you are
eating foods to which you are allergic or otherwise sensitive. Foods considered
to be friendly to eczema can cause flare-ups for people allergic to them. An
Anti-inflammatory Diet This eating plan focuses on eliminating foods that
contribute to inflammation while eating foods that are high in fiber.
Below is a list of foods that have
properties that can help reduce the flare-ups of eczema, but getting to know
your body and which foods are best for you, individually, is crucial. You might
be surprised to learn that there are all kinds of healthy foods that may
trigger problems.
Categories of foods that cause skin breakouts such as eczema
Seafood, as well as eggs, sugar, alcohol,
or gluten, tends to be high on the list of things not to eat for AD sufferers,
who swear consuming some foods triggers an AD skin breakout. Because
dyshidrotic eczema causes small blisters and cracked skin, you will want to
steer clear of acids—such as citrus fruits—that may trigger further irritation
to your skin.
To identify which foods might trigger a
food-sensitive reaction in eczema, your health care provider will usually
recommend an elimination diet. To identify what foods might be causing your
breakouts, try eliminating one of the common foods that trigger eczema for 14
days, and then introduce it back into the diet to see if it triggers reactions.
The elimination diet involves avoiding some of
the more common foods known to cause eczema. Anti-inflammatory diets are also
particularly useful for managing eczema symptoms, which may occur due to
stress, an immune system overreaction to an allergen, or environmental stimuli.
The most common way that foods may trigger skin conditions is if they cause skin breakouts. Skin reactions to foods may occur immediately, or they may take hours or even days to develop. Many eczema patients report reactions to foods, even when no real allergies are involved.
Those who developed eczema as infants or
in early childhood are most likely to have significant symptoms of a food allergy.
This could explain why food handlers who develop eczema are more likely to have
food allergies compared with those who have different jobs. Interestingly, food
allergies are most common in those with eczema; up to 30% of children younger
than five who have eczema are also likely to have at least one food allergy.
The body reacts to a particular food as
though it is harmful or dangerous, triggering symptoms like hives, itchiness,
and swelling, as well as mouth tingling, coughing, and vomiting. For others,
eating some foods, such as sugar, eggs, or dairy products, does not necessarily
kill them but causes eruptions of angry skin or eczema. For others, eating or
simply touching a particular food can trigger their skin to respond
(allergy-contact dermatitis). This is particularly the case if you are eating a
food that you are allergic to or otherwise sensitized to.










.jpg)


No comments:
Post a Comment